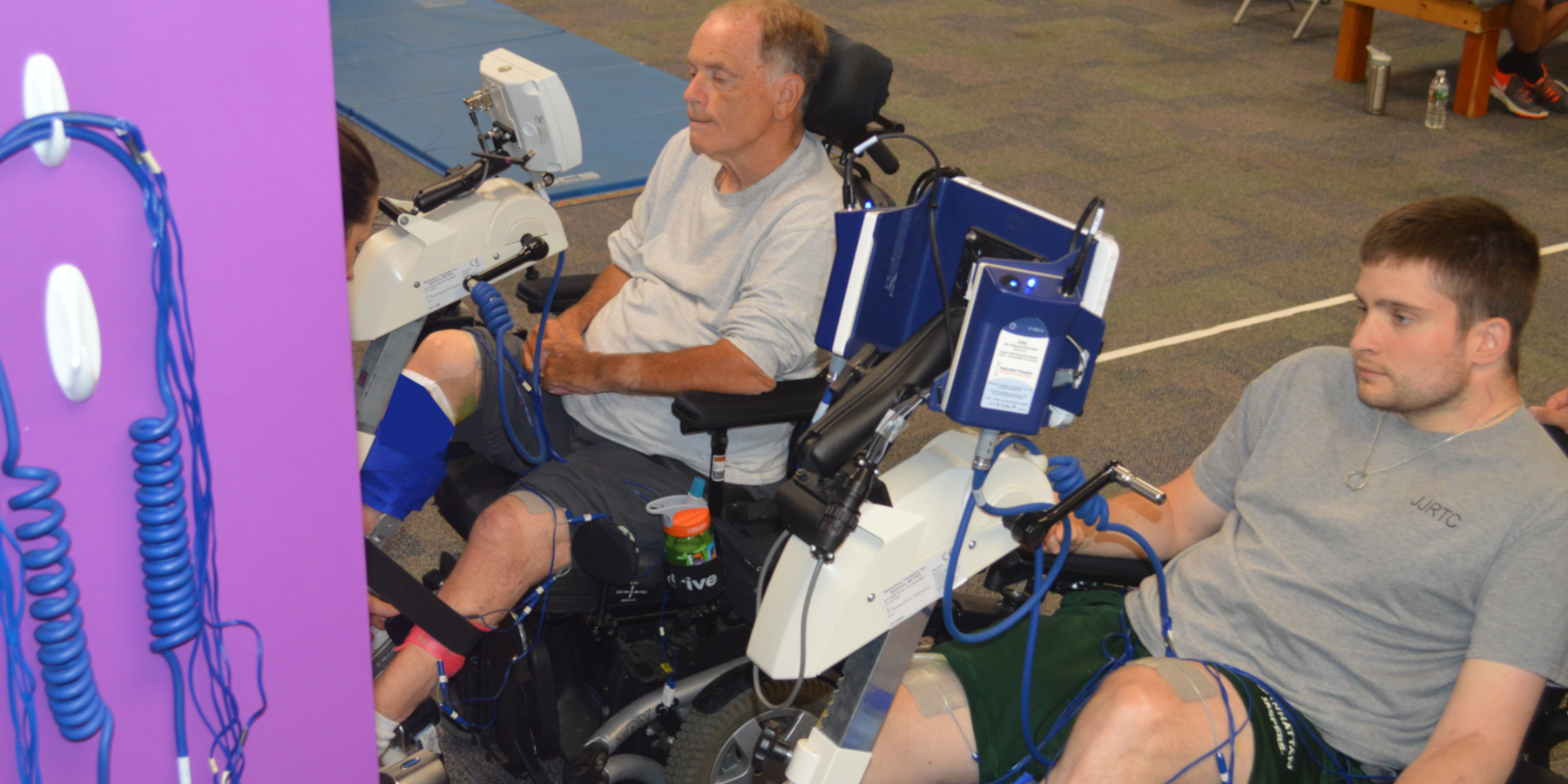
Upper and Lower Extremity Functional Electrical Stimulation (FES)
Upper and Lower Extremity Functional Electrical Stimulation (FES) is a rehabilitation technique whereby electrical current stimulates nerves to evoke muscle contractions. FES creates patterned movement of the legs and arms, enabling the muscles to work and perform active cycling to increase muscle mass.
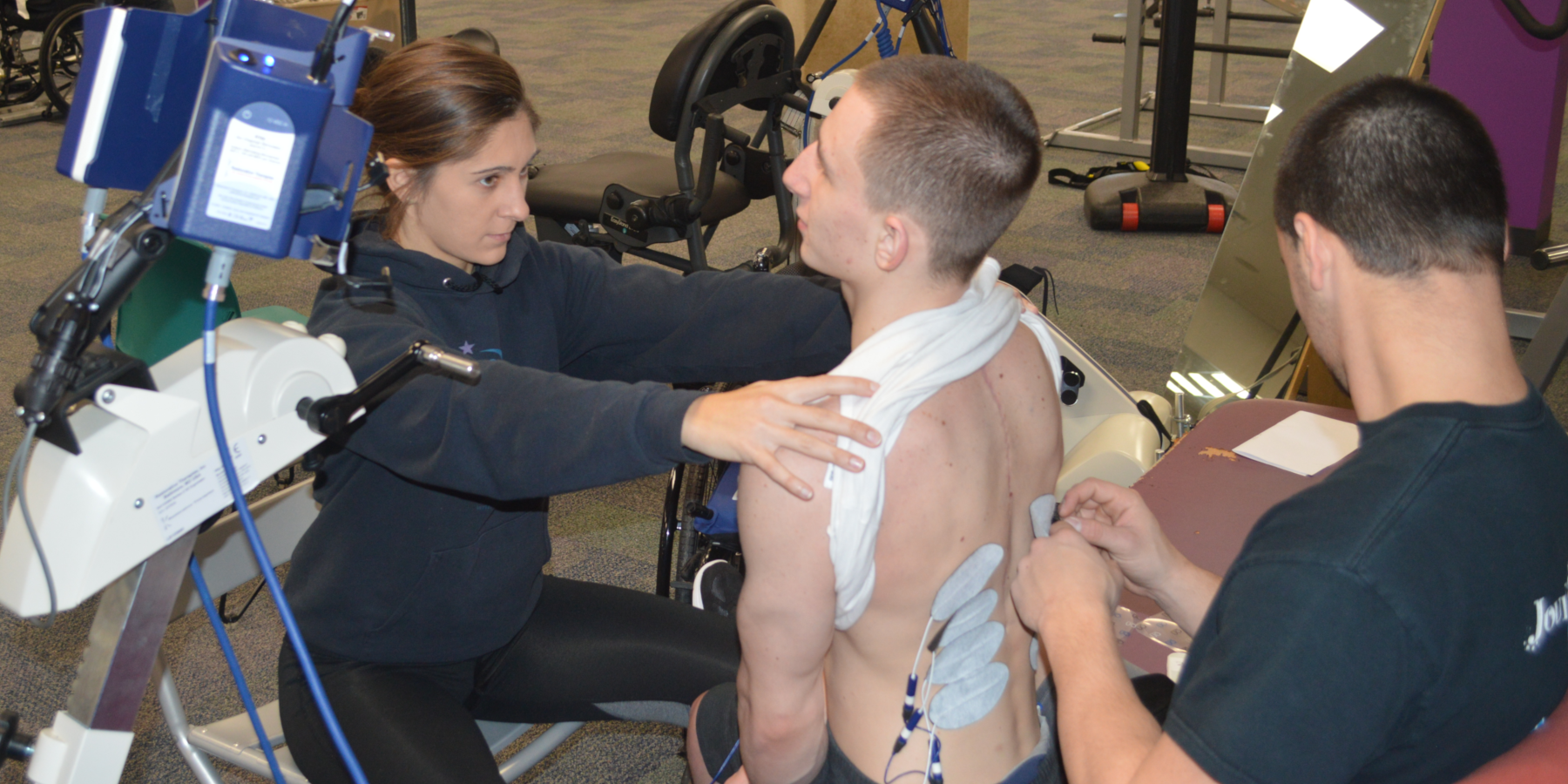
NeuroMuscular Electrical Stimulation (NMES)
NeuroMuscular Electrical Stimulation (NMES) is a form of activity-based rehabilitation that uses pulses of electrical current to evoke muscle contractions and patterned muscle activity to complete a specific task. Electrical stimulation enables muscles to work and perform activities even though the muscles may be weak or paralyzed through neurological disease or injury.
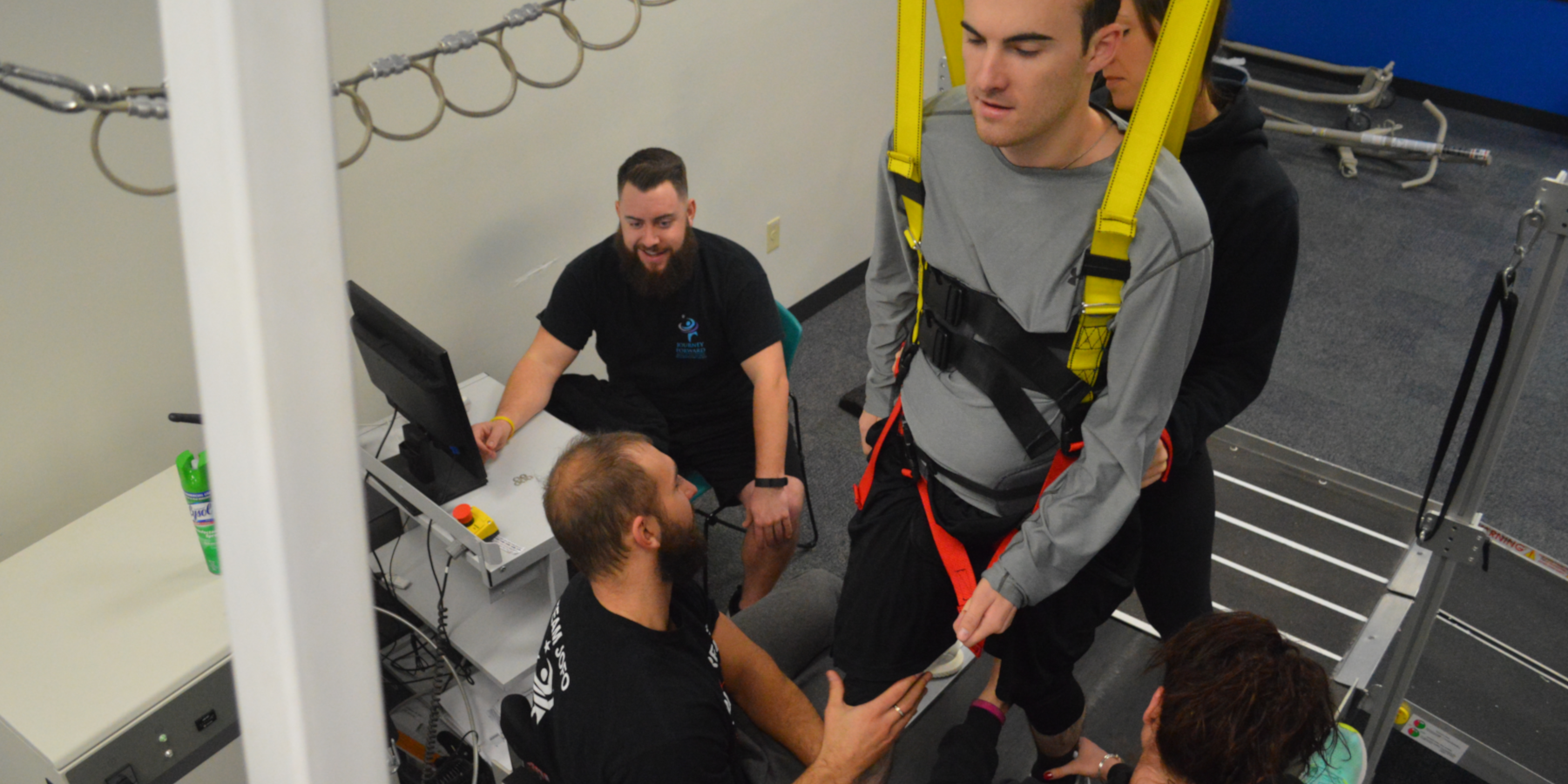

Locomotor Training
Locomotor Training is a rehabilitation strategy that allows individuals to repetitively practice standing and stepping using body weight support and a treadmill with manual facilitation from our Specialists.
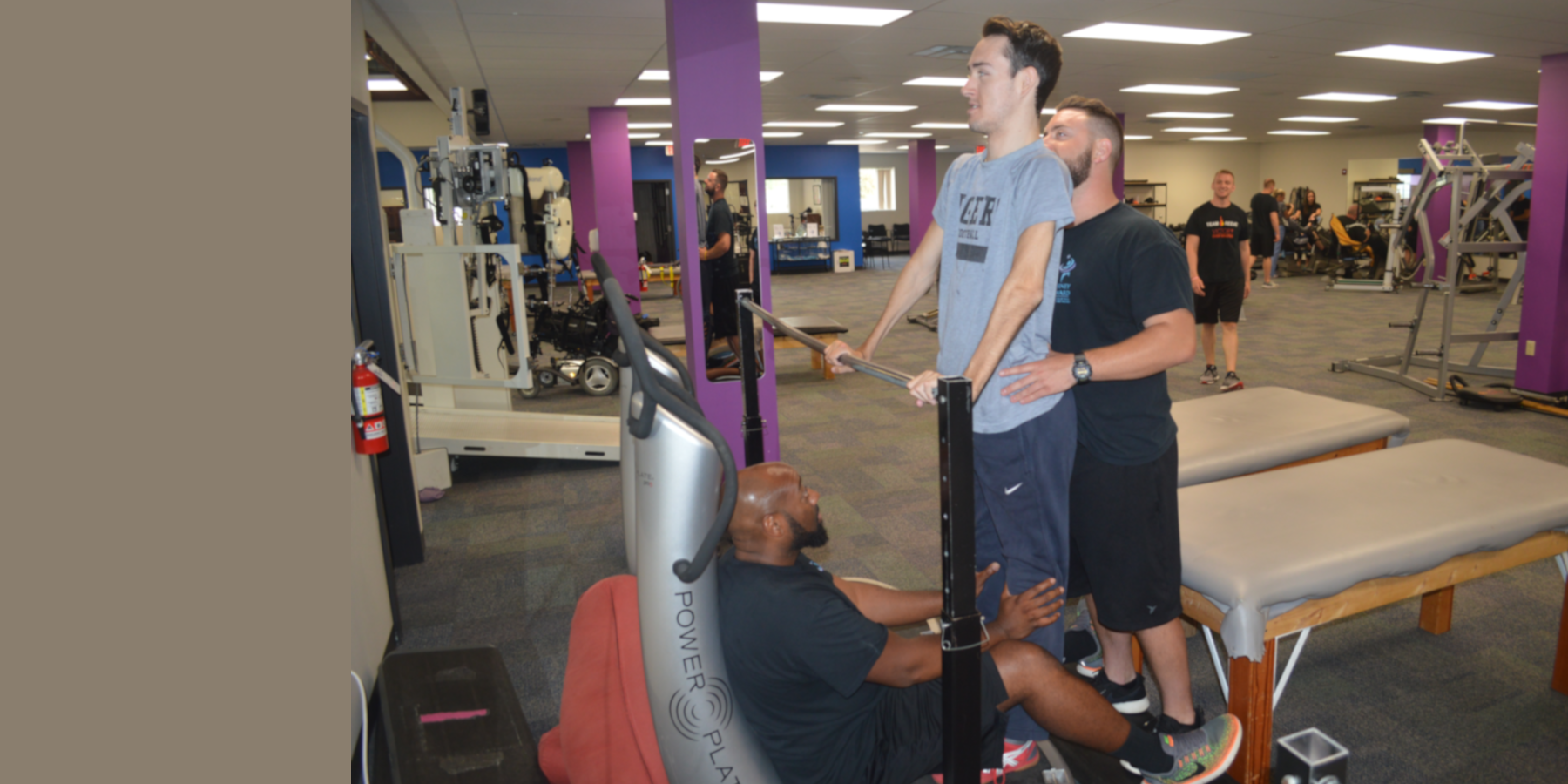

Vibration Training
Vibration Training allows even greater demand to be forced on the body. Many will experience an increase in sensation and function when performing activities while vibration training. Vibration training will also incorporate aspects of load bearing and has also shown many of the same benefits.
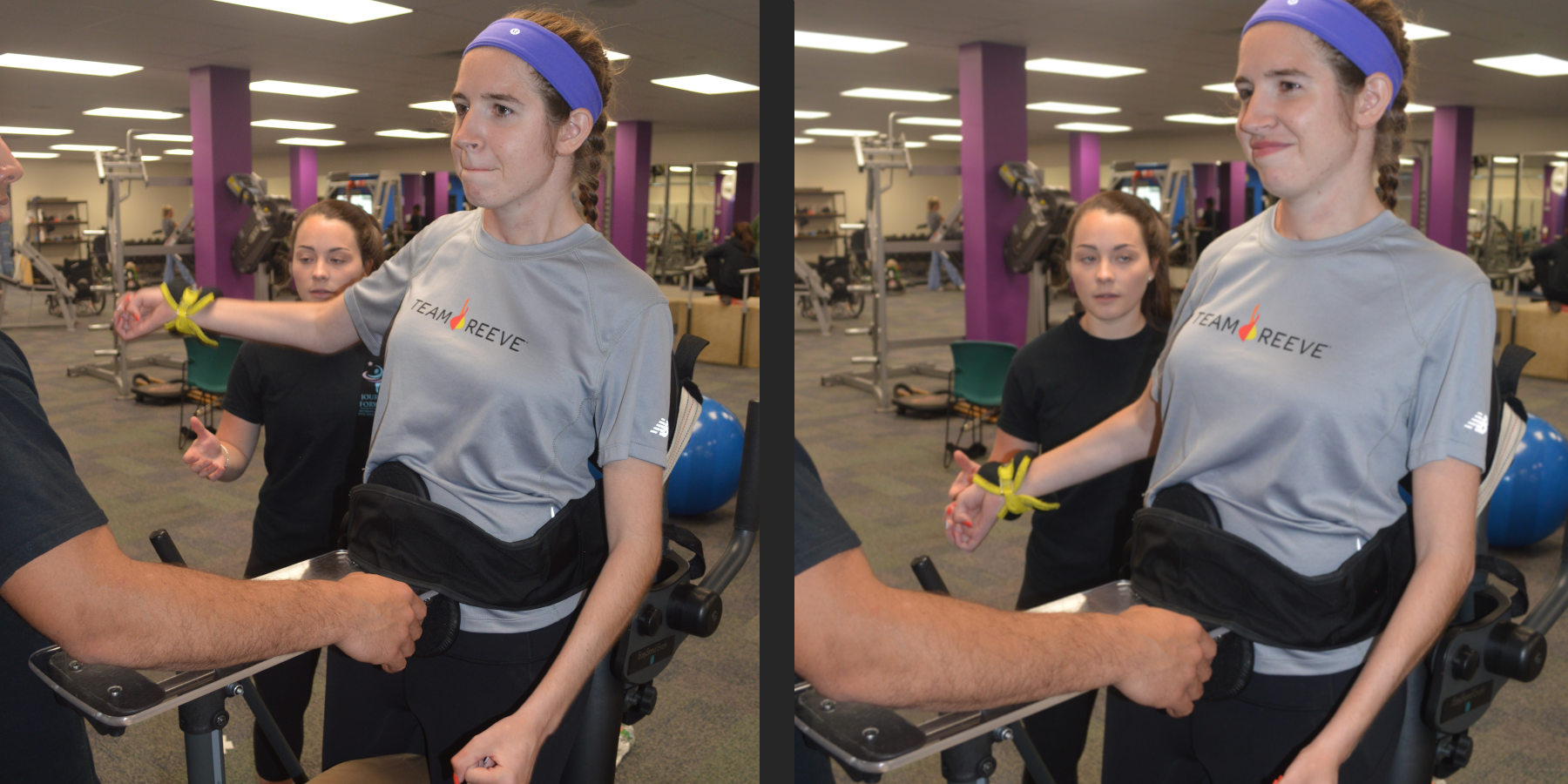

Guided Exercise
Guided Exercise is focused on the neuromuscular system below the level of injury or affected by paralysis. The client works one on one with a highly trained activity-based specialist. During these sessions the specialist will focus on the client’s needs and key factors promoting strength and independence. Movements related to daily motor tasks are the focus including trunk control and mobility, reaching and grasping and/or standing and walking.
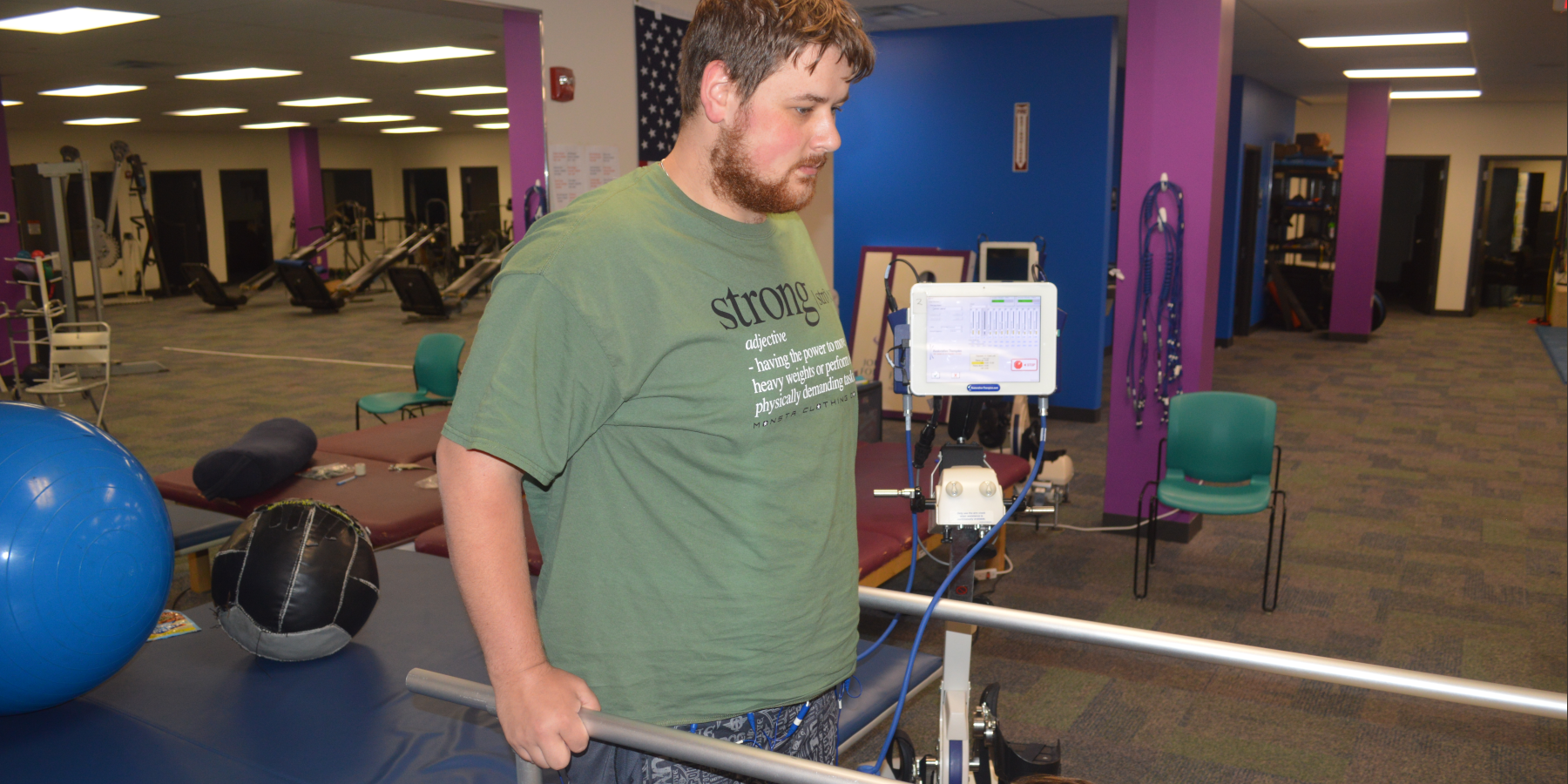

Load Bearing
Getting into the Load Bearing positions is a key aspect of recovery. This allows the nervous system to experience the stress of bearing the body’s weight. This has been shown to have positive benefits including improved bone density, greater stress on the muscles, and an increase in nervous system adaptations.


